Posted inQuestion about Japan
Why is Japan population decline?
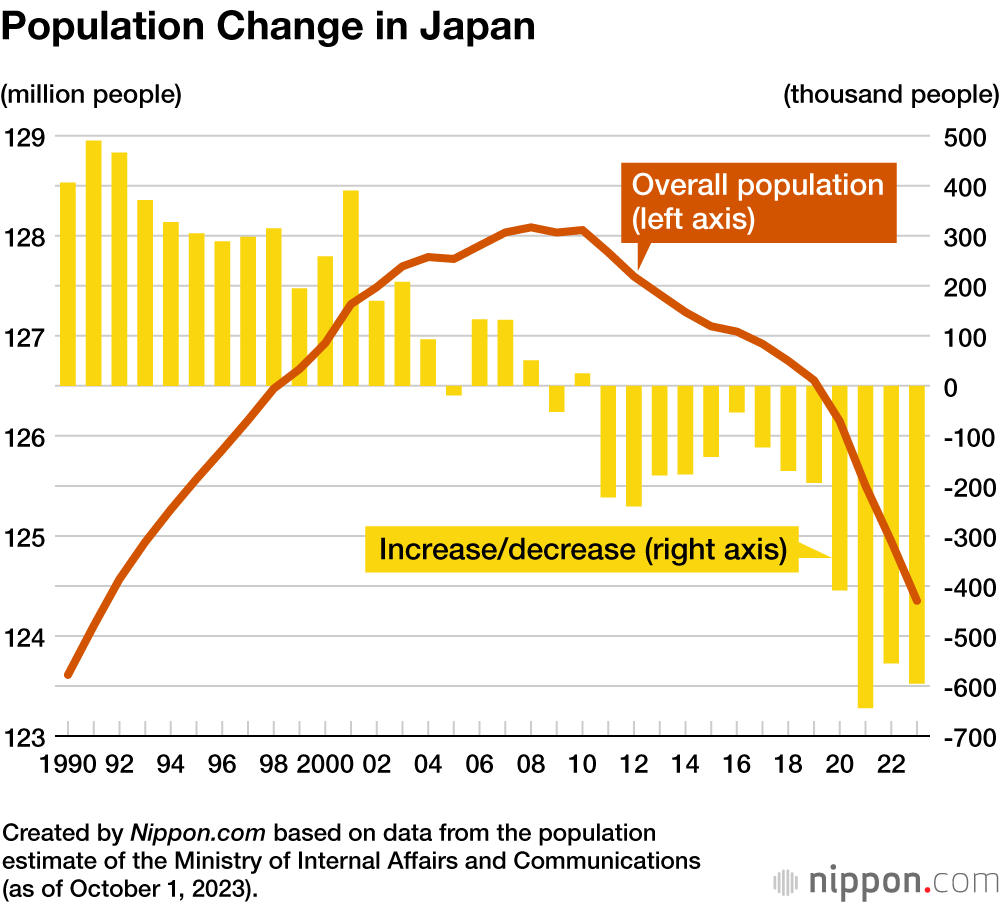
Japan's population decline is caused by a combination of factors, including an aging population, low fertility rates, and a lack of immigration. The aging population is due to increased life expectancy and low fertility rates, while the low fertility rates are due to high education and career expectations for women, a lack of family-friendly policies in the workplace, and cultural attitudes towards marriage and parenthood. Japan has historically been a relatively closed society with limited immigration policies, leading to a lack of diversity in the population and a shortage of workers in certain industries. The economic challenges presented by the aging population and low fertility rates include a shrinking labor force that makes it difficult for businesses to find workers and puts a strain on social security systems. Other contributing factors include gender inequality, high cost of living, declining marriage rates, urbanization, intense work culture, competitive education system, and limited success of government policies aimed at addressing these issues.