Why does Japan get so many tsunamis?
Introduction
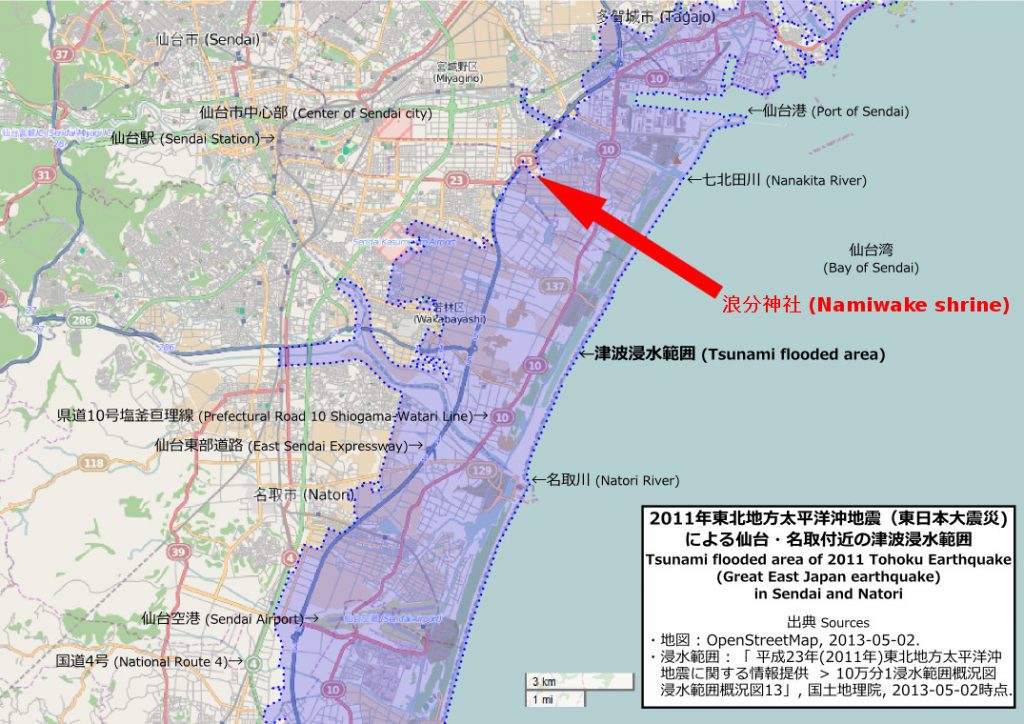
Japan is a country that is highly prone to tsunamis. This island country has been hit by some of the most devastating tsunamis in history, including the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami that killed over 15,000 people. The question is, why does Japan get so many tsunamis? In this article, we will explore the geographic and geological reasons that make Japan vulnerable to tsunamis.
The location of Japan
Japan is located in a region where several tectonic plates meet. The Pacific Plate, Philippine Plate, and Eurasian Plate all converge near Japan. This convergence results in frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions in the region, which can trigger tsunamis. Additionally, Japan’s position on the Pacific Ring of Fire makes it highly susceptible to seismic activity.

The shape of Japan’s coastline
Japan’s coastline is characterized by numerous bays, inlets, and peninsulas. These features create many narrow channels and shallow areas along the coast. When a tsunami hits these areas, the waves can amplify and become more destructive as they move inland. The shape of Japan’s coastline also means that tsunamis can travel farther inland than they would in a straighter coastline.
The size of Japan’s islands
Japan is made up of four main islands – Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku – and many smaller islands. The islands are relatively small and close together, which means that a tsunami can affect a large portion of the country at once. Furthermore, many of Japan’s cities are located along the coastlines of these islands, making them more vulnerable to tsunamis.
The depth of the sea floor
The sea floor around Japan is relatively shallow, which means that tsunamis can travel faster and with more force. When a tsunami approaches shallow waters, the wave height increases dramatically, resulting in greater damage to coastal areas. Additionally, the shallow sea floor can cause tsunamis to refract and reflect, leading to complex wave patterns that make it difficult to predict how a tsunami will behave.
The frequency of earthquakes
Japan experiences thousands of earthquakes every year, many of which are powerful enough to trigger tsunamis. The frequency of earthquakes in Japan means that the country has developed advanced earthquake and tsunami warning systems. However, even with these systems in place, it is impossible to predict every earthquake or tsunami.
The historical context
Japan’s history is filled with stories of devastating tsunamis. The country has experienced several major tsunamis throughout its history, including the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, the 1923 Great Kanto earthquake and tsunami, and the 1896 Meiji Sanriku earthquake and tsunami. These events have shaped Japanese culture and have led to a greater awareness of the dangers of tsunamis.
The impact of climate change
Climate change is causing sea levels to rise, which means that tsunamis could become more frequent and more destructive in the future. Rising sea levels also mean that coastal areas will be more vulnerable to flooding during a tsunami. Japan is taking steps to mitigate the effects of climate change and is working on improving its infrastructure to withstand future tsunamis.
The role of human activity
Human activity can also contribute to the frequency and severity of tsunamis. For example, the construction of dams and other structures can alter the flow of rivers and increase the risk of flooding during a tsunami. Additionally, coastal development can destroy natural barriers that protect against tsunamis, making these areas more vulnerable to damage.
The importance of preparedness
Given Japan’s susceptibility to tsunamis, it is crucial that the country is prepared for these events. Japan has invested heavily in early warning systems, evacuation plans, and disaster response teams. The government also conducts regular drills to ensure that people know how to respond in the event of a tsunami. Preparedness is key to minimizing the damage and loss of life caused by tsunamis.
The global context
Japan is not the only country that is vulnerable to tsunamis. Many other countries, particularly those located along the Pacific Ring of Fire, are at risk of these devastating events. By studying the causes and impacts of tsunamis in Japan, we can learn valuable lessons about how to prepare for and respond to these events in other parts of the world.
The future of Japan’s relationship with tsunamis
Tsunamis will continue to be a threat to Japan in the future. However, with advanced technology and better preparedness measures, Japan can minimize the impact of these events. Additionally, ongoing research into the causes and behavior of tsunamis can help us better understand and predict these events. It is important that we continue to learn from past experiences and work together to build a safer future for everyone.
Conclusion
Japan’s susceptibility to tsunamis is due to a combination of geographic, geological, and human factors. Despite this vulnerability, Japan has made significant strides in preparedness and response to these events. By studying the causes and impacts of tsunamis in Japan, we can gain valuable insights into how to mitigate the risks of these devastating events in other parts of the world.
How frequently do tsunamis happen in Japan?
Contrary to popular belief, tsunamis occur more frequently than most people realize. In fact, Japan experiences at least one tsunami per year. The majority of tsunamis, around 80%, occur in the Pacific Ocean, specifically in countries surrounding the “Pacific Ring of Fire”.
What country has the most tsunamis?
Indonesia, situated on the “ring of fire” in the Pacific Ocean, is prone to frequent earthquakes and volcanic activity. The country has experienced a total of 77 tsunamis, as recorded thus far.
Why is Japan so prone to natural disasters?
Due to its climate and topography, Japan is at risk of natural disasters. It is important to educate yourself on local protocols and measures for dealing with such events.
What is the tsunami capital of the world?
An interesting event happened in Hilo, often regarded as the global hub for tsunamis.
Has the US ever had a tsunami?
The United States has experienced large tsunamis in the past and it is likely that they will happen again. Powerful earthquakes in the Pacific rim have caused tsunamis to hit Hawaii, Alaska, and the west coast of the United States.
What is the number 1 worst tsunami?
The Indian Ocean tsunami that occurred on December 26, 2004, was the deadliest and most catastrophic tsunami ever recorded. It caused more than 230,000 deaths and affected people from 14 different countries, with Indonesia being the hardest hit, followed by Sri Lanka, India, and Thailand.
The need for continued research
Despite significant progress in understanding tsunamis, there is still much we don’t know about these events. Ongoing research is needed to better understand the behavior of tsunamis, predict their impacts, and develop new technologies to mitigate their effects. This research can help us better prepare for future tsunamis and reduce the risk of damage and loss of life.
The importance of international cooperation
Tsunamis are a global problem that requires international cooperation. Countries that are vulnerable to tsunamis can work together to share information, develop early warning systems, and coordinate disaster response efforts. By working together, we can better prepare for and respond to these devastating events.
The role of education
Education plays a crucial role in preparing people for tsunamis. Awareness campaigns can help people understand the risks and learn how to respond in the event of a tsunami. Schools can also incorporate tsunami preparedness into their curriculums, teaching students about the science behind tsunamis and how to stay safe during an event.
The need for sustainable development
Sustainable development is crucial for reducing the risk of damage and loss of life during a tsunami. Building in areas that are less vulnerable to tsunamis, preserving natural barriers such as mangroves and coral reefs, and developing early warning systems are all important steps towards sustainable development. By taking a long-term approach to development, we can reduce the impact of tsunamis on communities around the world.
The human cost of tsunamis
While we often think of tsunamis in terms of their physical impact, it’s important to remember the human cost of these events. Tsunamis can cause significant emotional trauma for survivors and can lead to long-term displacement and economic hardship. By focusing on the human impact of tsunamis, we can better understand the need for preparedness and sustainable development.